八月十七是什么星座
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI) is an on-chip communication bus protocol and is part of the Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture specification (AMBA).[1][2] AXI had been introduced in 2003 with the AMBA3 specification. In 2010, a new revision of AMBA, AMBA4, defined the AXI4, AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream protocols. AXI is royalty-free and its specification is freely available from ARM.
AMBA AXI specifies many optional signals, which can be included depending on the specific requirements of the design,[3] making AXI a versatile bus for numerous applications.
While the communication over an AXI bus is between a single initiator and a single target, the specification includes detailed descriptions and signals to include N:M interconnects, able to extend the bus to topologies with multiple initiators and targets.[4]
AMBA AXI4, AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream have been adopted by Xilinx and many of its partners as a main communication bus in their products.[5][6]
Thread IDs
[edit]Thread IDs allow a single initiator port to support multiple threads, where each thread has in-order access to the AXI address space, however each thread ID initiated from a single initiator port may complete out of order with respect to each other. For instance in the case where one thread ID is blocked by a slow peripheral, another thread ID may continue independently of the order of the first thread ID. Another example, one thread on a CPU may be assigned a thread ID for a particular initiator port memory access such as read addr1, write addr1, read addr1, and this sequence will complete in order because each transaction has the same initiator port thread ID. Another thread running on the CPU may have another initiator port thread ID assigned to it, and its memory access will be in order as well but may be intermixed with the first thread IDs transactions.
Thread IDs on an initiator port are not globally defined, thus an AXI switch with multiple initiator ports will internally prefix the initiator port index to the thread ID, and provide this concatenated thread ID to the target device, then on return of the transaction to its initiator port of origin, this thread ID prefix will be used to locate the initiator port and the prefix will be truncated. This is why the target port thread ID is wider in bits than the initiator port thread ID.
AXI-Lite bus is an AXI bus that only supports a single ID thread per initiator. This bus is typically used for an end point that only needs to communicate with a single initiator device at a time, for example, a simple peripheral such as a UART. In contrast, a CPU is capable of initiating transactions to multiple peripherals and address spaces at a time, and will support more than one thread ID on its AXI initiator ports and AXI target ports. This is why a CPU will typically support a full spec AXI bus. A typical example of a front side AXI switch would include a full specification AXI initiator connected to a CPU initiator, and several AXI-Lite targets connected to the AXI switch from different peripheral devices.
(Additionally, the AXI-Lite bus is restricted to only support transaction lengths of a single data word per transaction.)
Handshake
[edit]
AXI defines a basic handshake mechanism, composed by an xVALID and xREADY signal.[7] The xVALID signal is driven by the source to inform the destination entity that the payload on the channel is valid and can be read from that clock cycle onwards. Similarly, the xREADY signal is driven by the receiving entity to notify that it is prepared to receive data.
When both the xVALID and xREADY signals are high in the same clock cycle, the data payload is considered transferred and the source can either provide a new data payload, by keeping high xVALID, or terminate the transmission, by de-asserting xVALID. An individual data transfer, so a clock cycle when both xVALID and xREADY are high, is called "beat".
Two main rules are defined for the control of these signals:
- A source must not wait for a high
xREADYto assertxVALID. - Once
xVALIDis asserted, a source must maintain the assertion until a handshake occurs.
Thanks to this handshake mechanism, both the source and the destination can control the flow of data, throttling the speed if needed.
Channels
[edit]In the AXI specification, five channels are described:[8]
- Read Address channel (AR)
- Read Data channel (R)
- Write Address channel (AW)
- Write Data channel (W)
- Write Response channel (B)
Other than some basic ordering rules,[9] each channel is independent from each other and has its own couple of xVALID/xREADY handshake signals.[10]
AXI
[edit]Signals
[edit]| Signal description | Write Address channel | Read Address channel |
|---|---|---|
| Address ID, to identify multiple streams over a single channel | AWID | ARID |
| Address of the first beat of the burst | AWADDR | ARADDR |
| Number of beats inside the burst | AWLEN[nb 1] | ARLEN[nb 1] |
| Size of each beat | AWSIZE | ARSIZE |
| Type of the burst | AWBURST | ARBURST |
| Lock type, to provide atomic operations | AWLOCK[nb 1] | ARLOCK[nb 1] |
| Memory type, how the transaction has to progress through the system | AWCACHE | ARCACHE |
| Protection type: privilege, security level and data/instruction access | AWPROT | ARPROT |
| Quality of service of the transaction | AWQOS[nb 2] | ARQOS[nb 2] |
| Region identifier, to access multiple logical interfaces from a single physical one | AWREGION[nb 2] | ARREGION[nb 2] |
| User-defined data | AWUSER[nb 2] | ARUSER[nb 2] |
xVALID handshake signal |
AWVALID | ARVALID |
xREADY handshake signal |
AWREADY | ARREADY |
| Signal description | Write Data channel | Read Data channel |
|---|---|---|
| Data ID, to identify multiple streams over a single channel | WID[nb 3] | RID |
| Read/Write data | WDATA | RDATA |
| Read response, to specify the status of the current RDATA signal | RRESP | |
| Byte strobe, to indicate which bytes of the WDATA signal are valid | WSTRB | |
| Last beat identifier | WLAST | RLAST |
| User-defined data | WUSER[nb 2] | RUSER[nb 2] |
xVALID handshake signal |
WVALID | RVALID |
xREADY handshake signal |
WREADY | RREADY |
| Signal description | Write Response channel |
|---|---|
| Write response ID, to identify multiple streams over a single channel | BID |
| Write response, to specify the status of the burst | BRESP |
| User-defined data | BUSER[nb 2] |
xVALID handshake signal |
BVALID |
xREADY handshake signal |
BREADY |
Bursts
[edit]
AXI is a burst-based protocol,[12] meaning that there may be multiple data transfers (or beats) for a single request. This makes it useful in the cases where it is necessary to transfer large amount of data from or to a specific pattern of addresses. In AXI, bursts can be of three types, selected by the signals ARBURST (for reads) or AWBURST (for writes):[13]
- FIXED
- INCR
- WRAP
In FIXED bursts, each beat within the transfer has the same address. This is useful for repeated access at the same memory location, such as when reading or writing a FIFO.
In INCR bursts, on the other hand, each beat has an address equal to the previous one plus the transfer size. This burst type is commonly used to read or write sequential memory areas.
WRAP bursts are similar to the INCR ones, as each transfer has an address equal to the previous one plus the transfer size. However, with WRAP bursts, if the address of the current beat reaches the "Higher Address boundary", it is reset to the "Wrap boundary":
with
Transactions
[edit]Reads
[edit]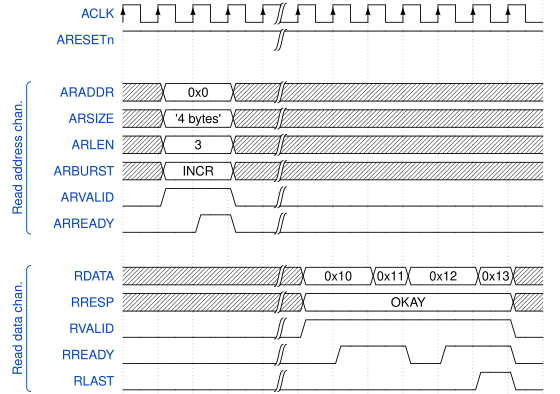
To start a read transaction, the initiator has to provide on the Read address channel:
- the start address on ARADDR
- the burst type, either FIXED, INCR or WRAP, on ARBURST (if present)
- the burst length on ARLEN (if present).
Additionally, the other auxiliary signals, if present, are used to define more specific transfers.
After the usual ARVALID/ARREADY handshake, the target has to provide on the Read data channel:
- the data corresponding to the specified address(es) on RDATA
- the status of each beat on RRESP
plus any other optional signals. Each beat of the target's response is done with a RVALID/RREADY handshake and, on the last transfer, the target has to assert RLAST to inform that no more beats will follow without a new read request.
Writes
[edit]
To start a write operation, the initiator has to provide both the address information and the data ones.
The address information are provided over the Write address channel, in a similar manner as a read operation:
- the start address has to be provided on AWADDR
- the burst type, either FIXED, INCR or WRAP, on AWBURST (if present)
- the burst length on AWLEN (if present)
and, if present, all the optional signals.
An initiator has also to provide the data related to the specified address(es) on the Write data channel:
- the data on WDATA
- the "strobe" bits on WSTRB (if present), which conditionally mark the individual WDATA bytes as "valid" or "invalid"
Like in the read path, on the last data word, WLAST has to be asserted by the initiator.
After the completion of both the transactions, the target has to send back to the initiator the status of the write over the Write response channel, by returning the result over the BRESP signal.
AXI4-Lite
[edit]AXI4-Lite is a subset of the AXI4 protocol, providing a register-like structure with reduced features and complexity.[15] Notable differences are:
- all bursts are composed by 1 beat only
- all data accesses use the full data bus width, which can be either 32 or 64 bits
AXI4-Lite removes part of the AXI4 signals but follows the AXI4 specification for the remaining ones. Being a subset of AXI4, AXI4-Lite transactions are fully compatible with AXI4 devices, permitting the interoperability between AXI4-Lite initiators and AXI4 targets without additional conversion logic.[16]
Signals
[edit]| Write address channel | Write data channel | Write response channel | Read address channel | Read data channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWVALID | WVALID | BVALID | ARVALID | RVALID |
| AWREADY | WREADY | BREADY | ARREADY | RREADY |
| AWADDR | WDATA | BRESP | ARADDR | RDATA |
| AWPROT | WSTRB | ARPROT | RRESP |
AXI-Stream
[edit]AXI4-Stream is a simplified, lightweight bus protocol designed specifically for high-speed streaming data applications. It supports only unidirectional data flow, without the need for addressing or complex handshaking. An AXI Stream is similar to an AXI write data channel, with some important differences on how the data is arranged:
- no bursts, instead data is packed into packets, frames and data streams
- no limit on the data length which may be continuous
- data width can be any integer number of bytes
AXI5 Stream protocol introduces wake-up signaling and signal protection using parity.
A single AXI Stream transmitter can drive multiple streams which may be interleaved but reordering is not permitted.
| Signal | Source | Width | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACLK | Clock | 1 | ACLK is a global clock signal. All signals are sampled on the rising edge of ACLK. |
| ARESETn | Reset | 1 | ARESETn is a global reset signal. |
| TVALID | Transmitter | 1 | TVALID indicates the Transmitter is driving a valid transfer. A transfer takes place when both TVALID and TREADY are asserted. |
| TREADY | Receiver | 1 | TREADY indicates that a Receiver can accept a transfer. |
| TDATA | Transmitter | TDATA_WIDTH | TDATA is the primary payload used to provide the data that is passing across the interface. TDATA_WIDTH must be an integer number of bytes and is recommended to be 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512 or 1024-bits. |
| TSTRB | Transmitter | TDATA_WIDTH/8 | TSTRB is the byte qualifier that indicates whether the content of the associated byte of TDATA is processed as a data byte or a position byte. |
| TKEEP | Transmitter | TDATA_WIDTH/8 | TKEEP is the byte qualifier that indicates whether content of the associated byte of TDATA is processed as part of the data stream. |
| TLAST | Transmitter | 1 | TLAST indicates the boundary of a packet. |
| TID | Transmitter | TID_WIDTH | TID is a data stream identifier. TID_WIDTH is recommended to be no more than 8. |
| TDEST | Transmitter | TDEST_WIDTH | TDEST provides routing information for the data stream. TDEST_WIDTH is recommended to be no more than 8. |
| TUSER | Transmitter | TUSER_WIDTH | TUSER is a user-defined sideband information that can be transmitted along the data stream. TUSER_WIDTH is recommended to be an integer multiple of TDATA_WIDTH/8. |
| TWAKEUP | Transmitter | 1 | TWAKEUP identifies any activity associated with AXI-Stream interface. |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "AMBA | Documentation". Arm Holdings.
- ^ Toole, Christina (24 October 2016). "Introduction to AXI Protocol: Understanding the AXI interface". arm.com. Arm Limited. Retrieved 11 September 2023.
The protocol used by many SoC designers today is AXI, or Advanced eXtensible Interface, and is part of the Arm Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) specification. It is especially prevalent in Xilinx's Zynq devices, providing the interface between the processing system and programmable logic sections of the chip.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 109–118. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 23–24. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ "AMBA AXI4 Interface Protocol". www.xilinx.com. Xilinx Inc.
- ^ "AXI4 IP". www.xilinx.com. Xilinx Inc.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 37–38. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 22–23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 40. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 38. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 28–34. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 22. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 45–47. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ a b Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 44. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. pp. 121–128. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 124. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Arm Holdings. "AMBA AXI and ACE Protocol Specification" (PDF). developer.arm.com. p. 122. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 July 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2019.






